Salmonella is a rod-shaped, gram-negative, non-spore forming bacteria that cause illnesses in humans and many animals, such as typhoid fever, paratyphoid fever, and salmonellosis which comes from eating contaminated food.
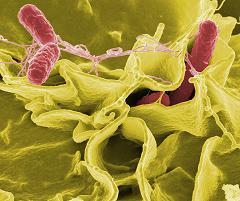
Salmonella infections are zoonotic, which means it can be transmitted by humans to animals and vice versa, and this includes food.
People at risk of infections are infants, small children, the elderly, and salmonella can become very serious, leading to complications.
Unclean food, particularly in kitchens and restaurants, is the one source of infection which can be prevented by providing sanitary preparation conditions.
Salmonella got its name from Dr. Daniel Elmer Salmon, an American veterinarian who isolated one type of the bacteria in 1885.
