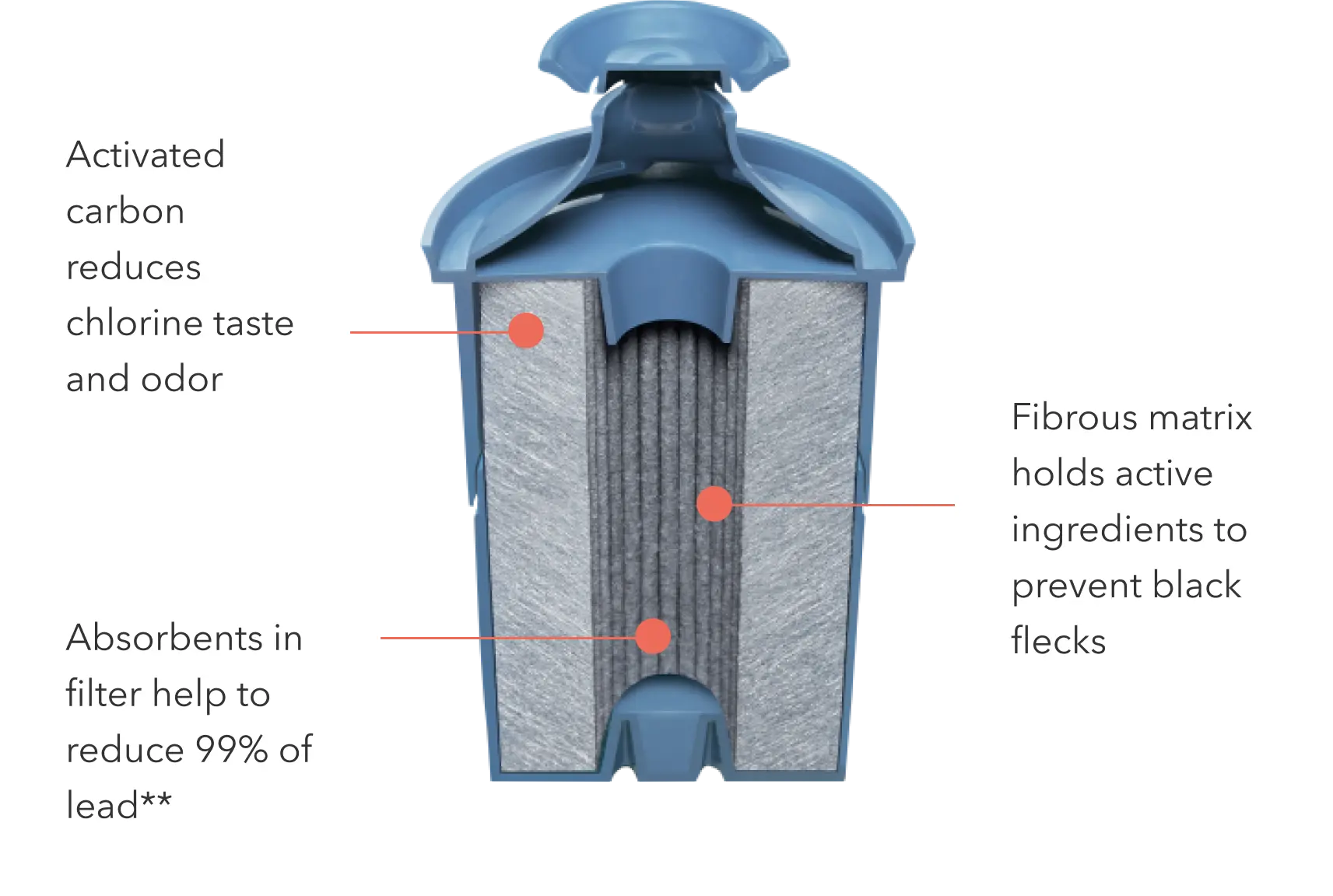
What Does Prime Beef Mean and Where Does Prime Rib Come From?
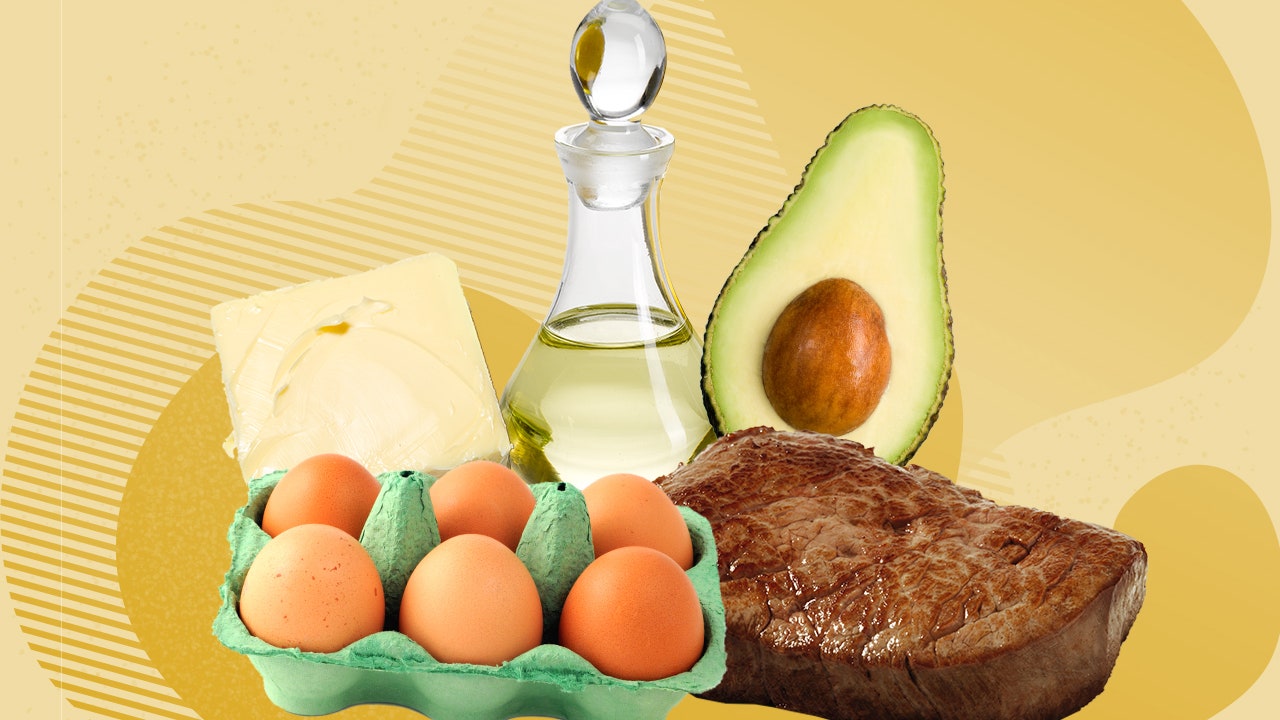
USDA Prime is indeed the finest and most expensive grade of beef. But we have all at one time or another been subjected to a $5.95 (salad bar included) slab of tough, dry “prime rib” rimmed with vulcanized-rubber fat that clearly deserved to be stamped “USDA Inedible.” Is there some misrepresentation going on here? Not … Read more