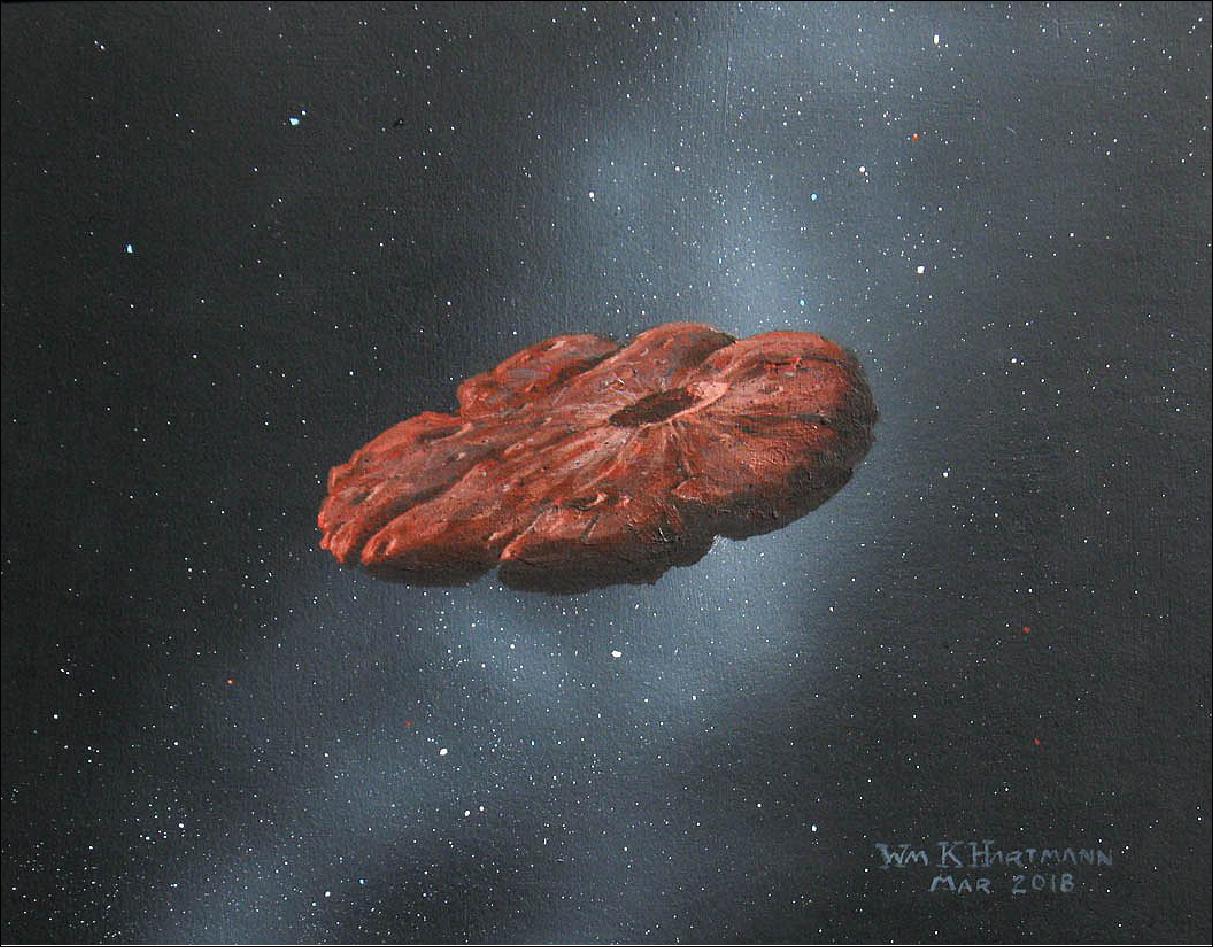
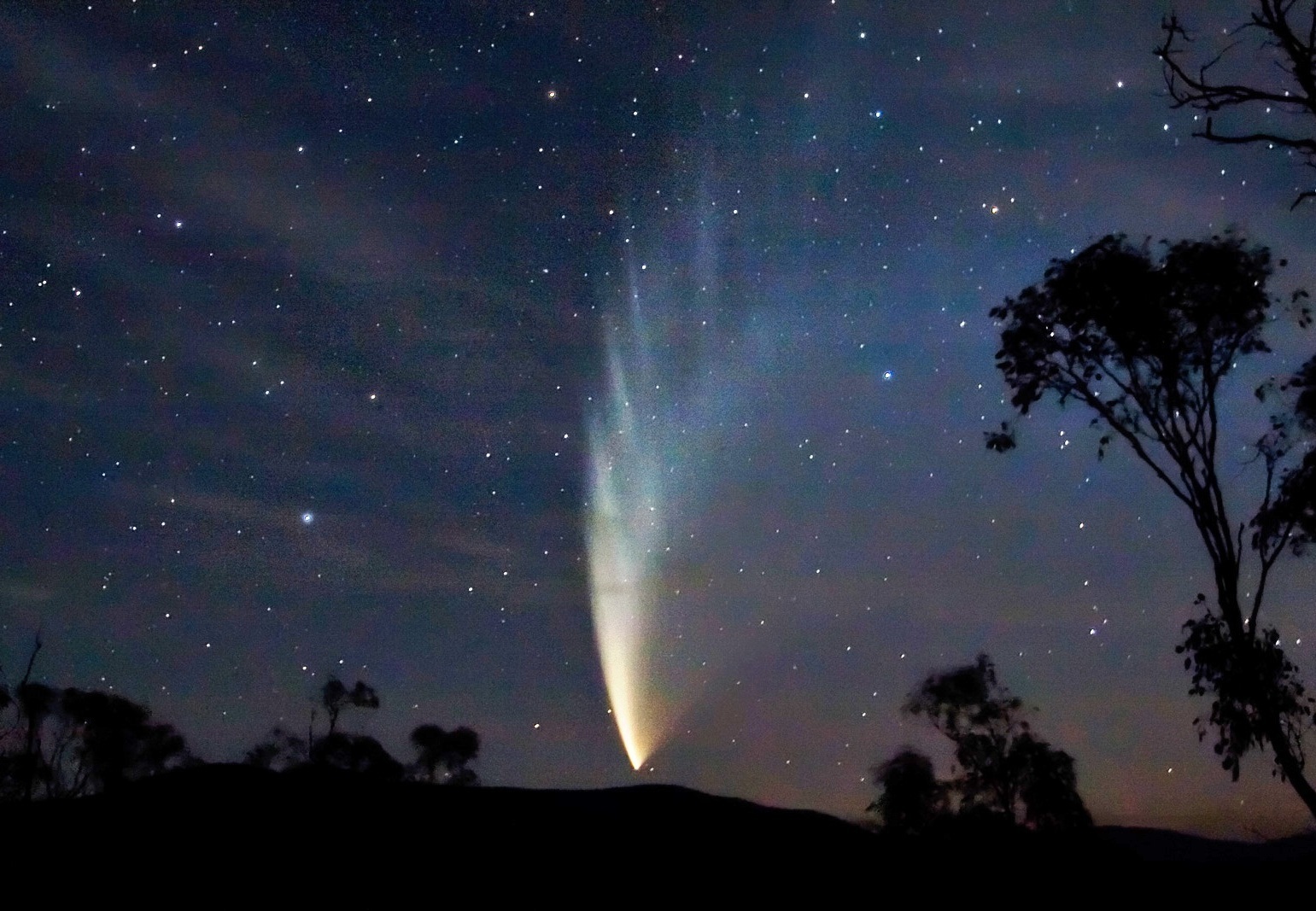
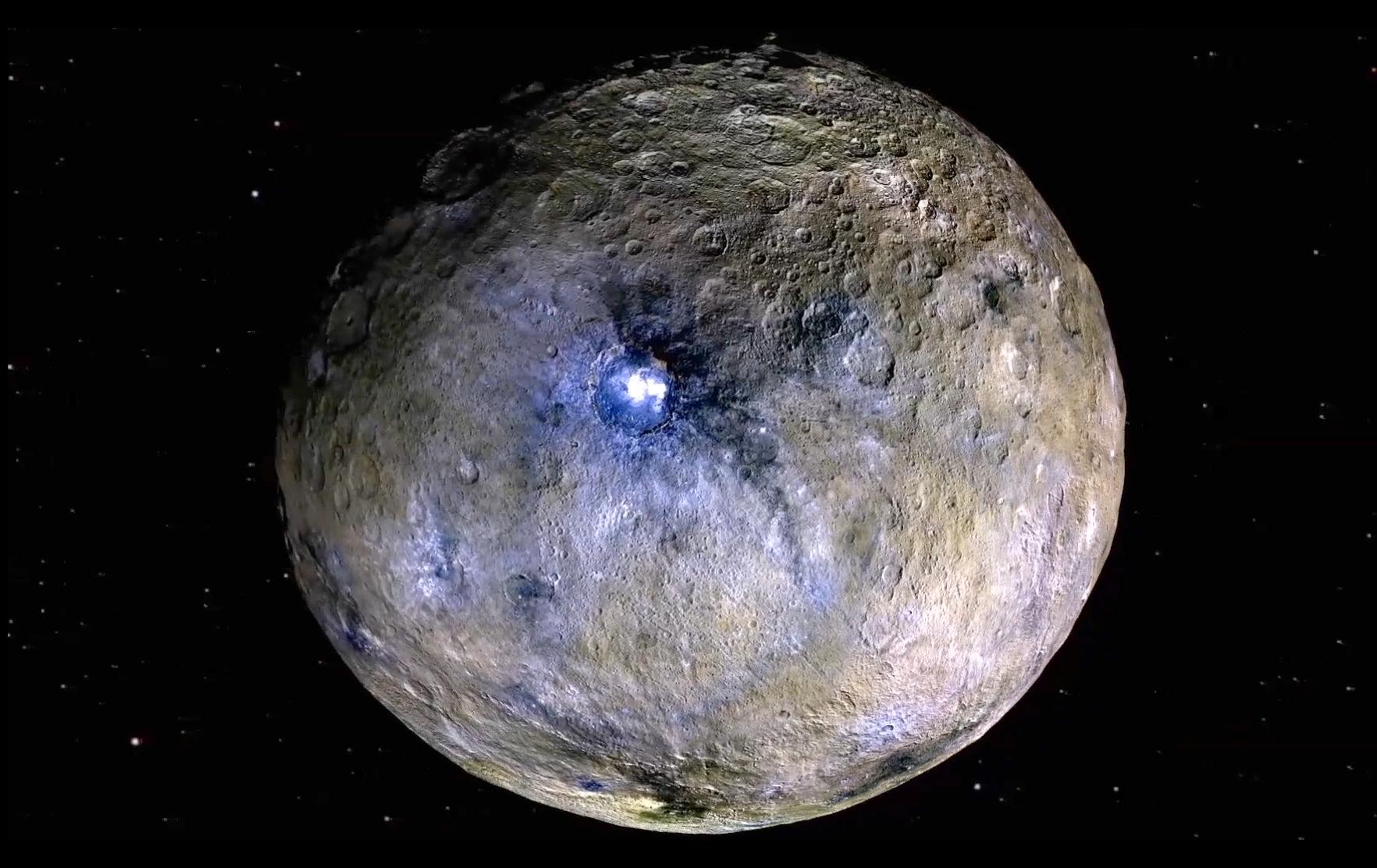
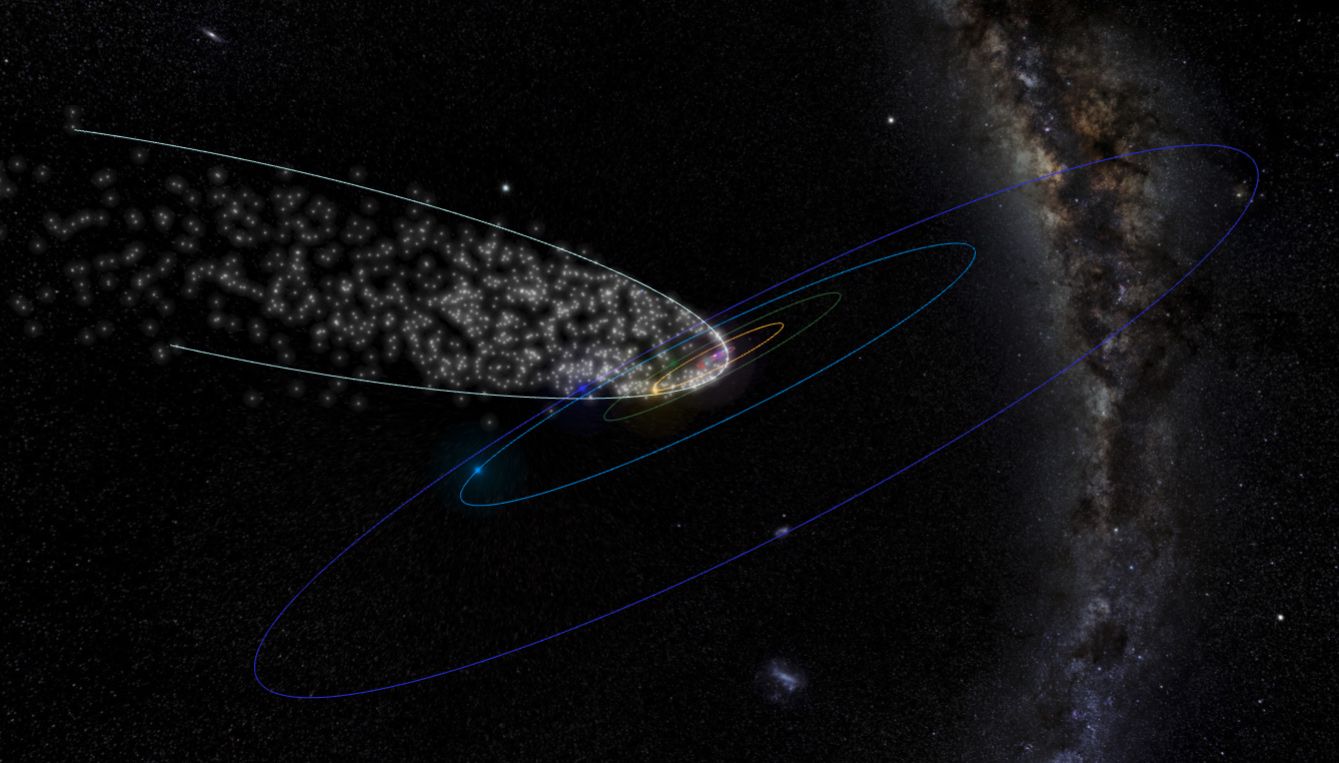
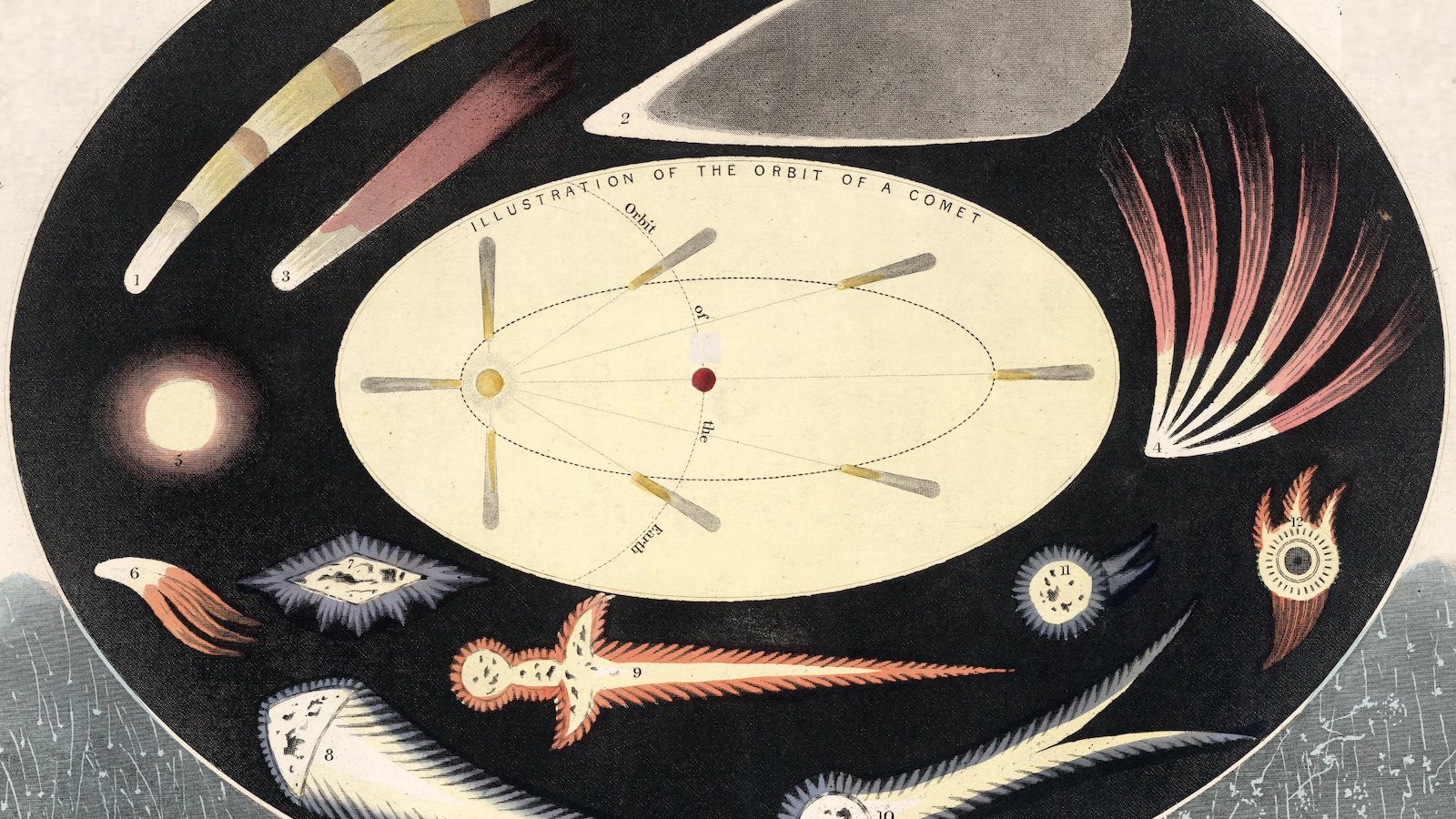
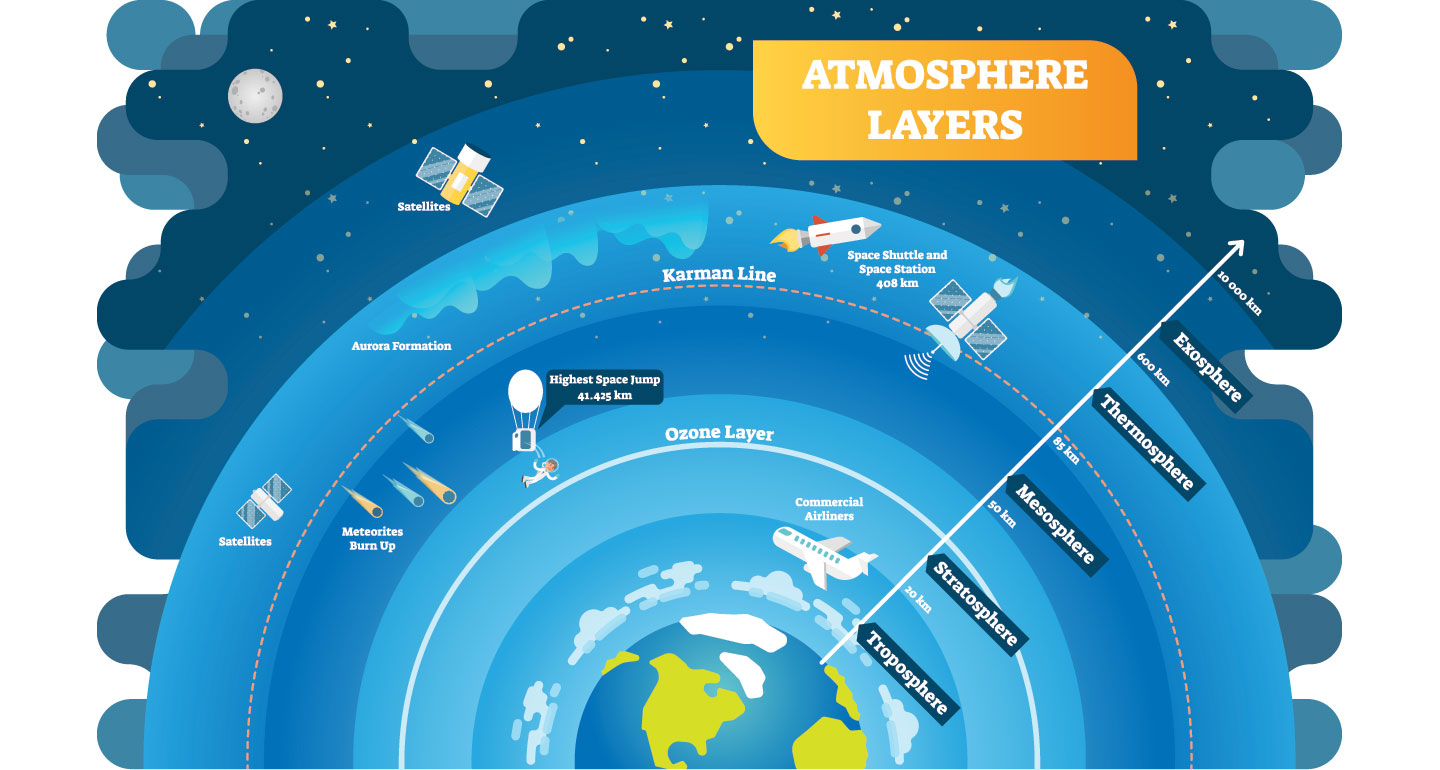
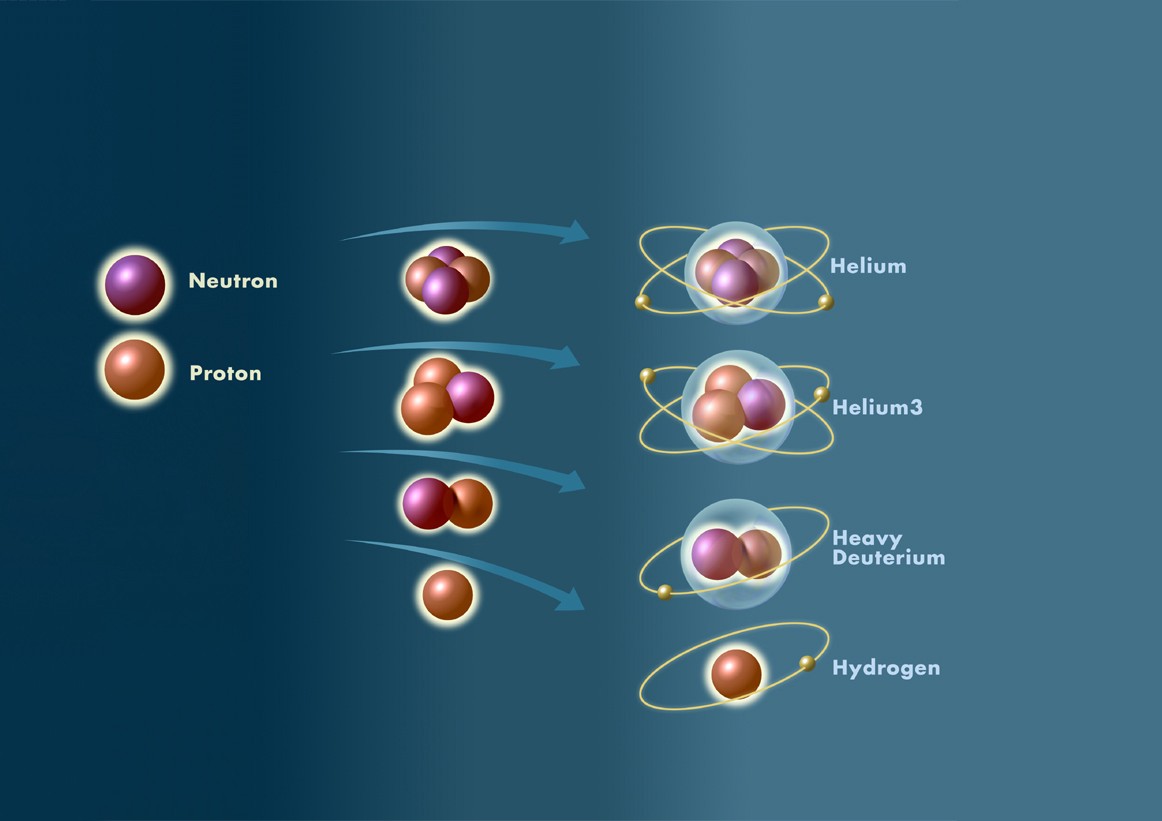
How Long Do Comets Live For and Do Comets Last Forever When They Leave the Solar System?
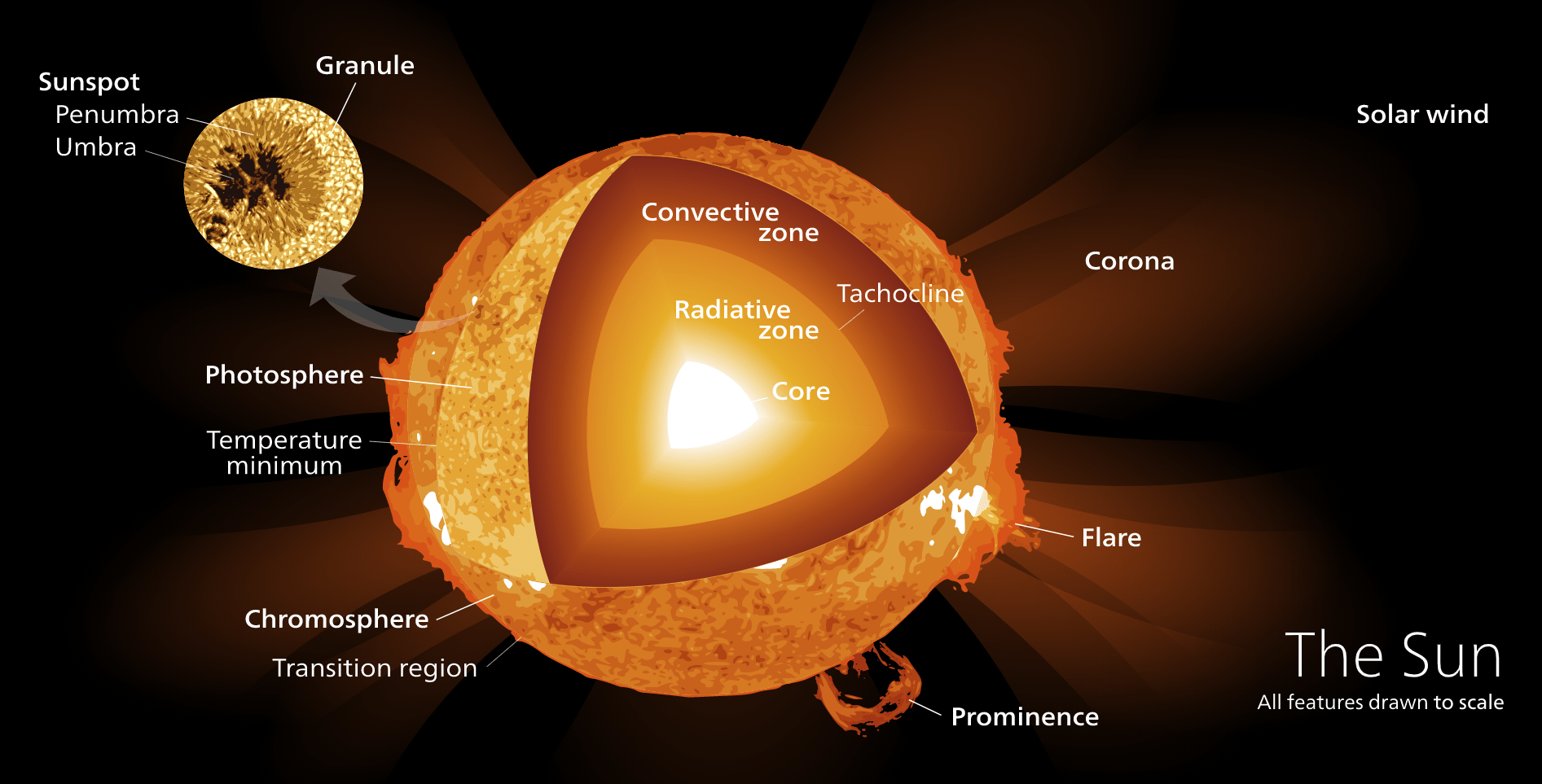
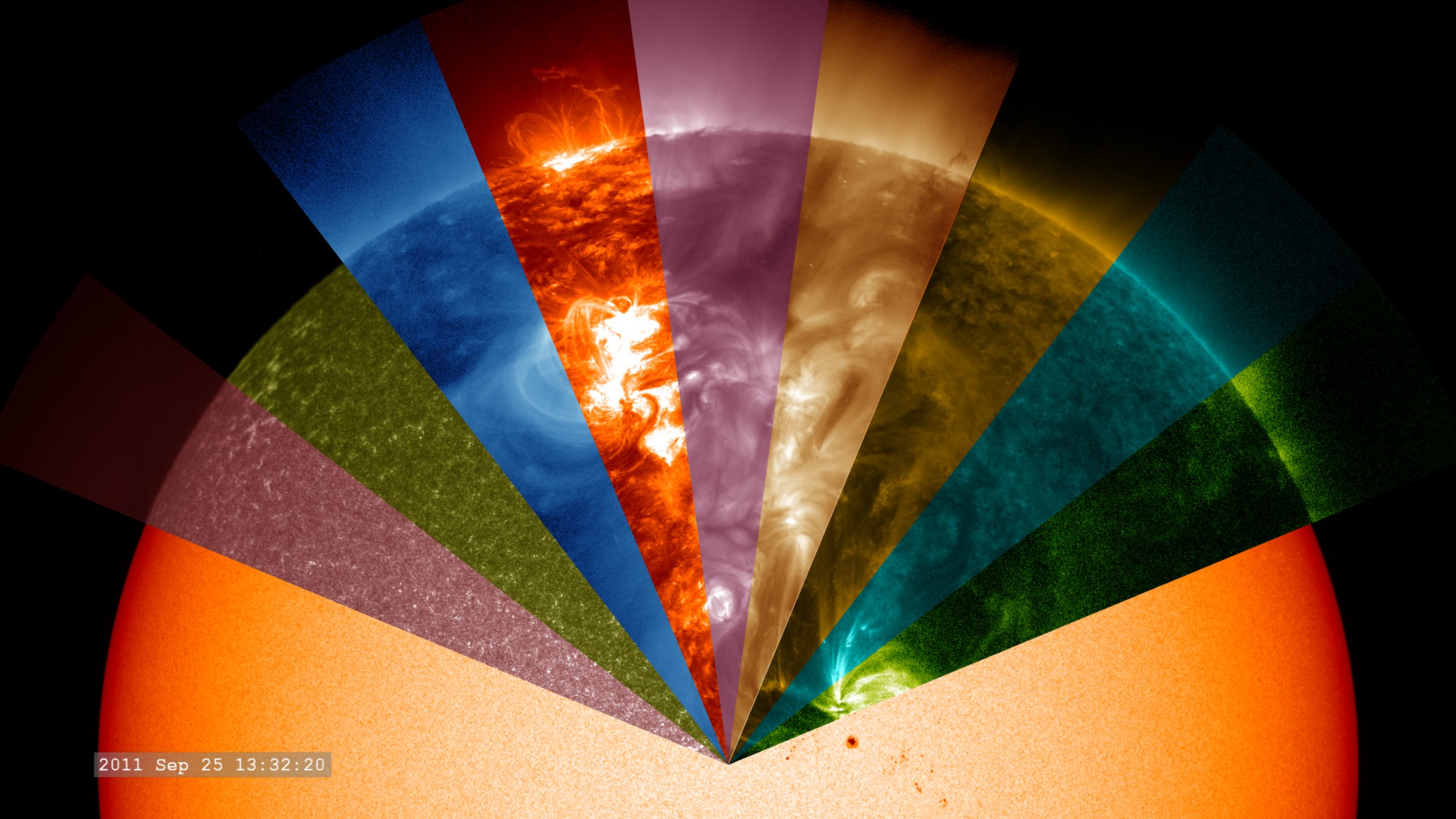
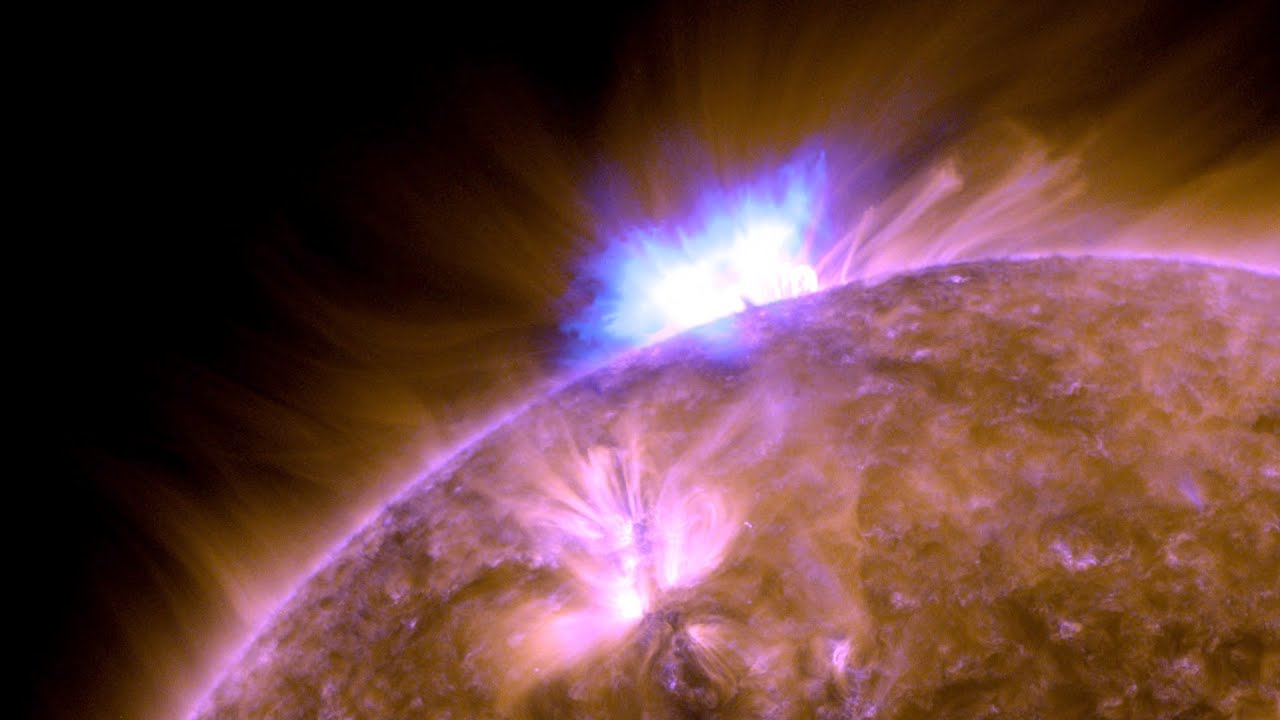
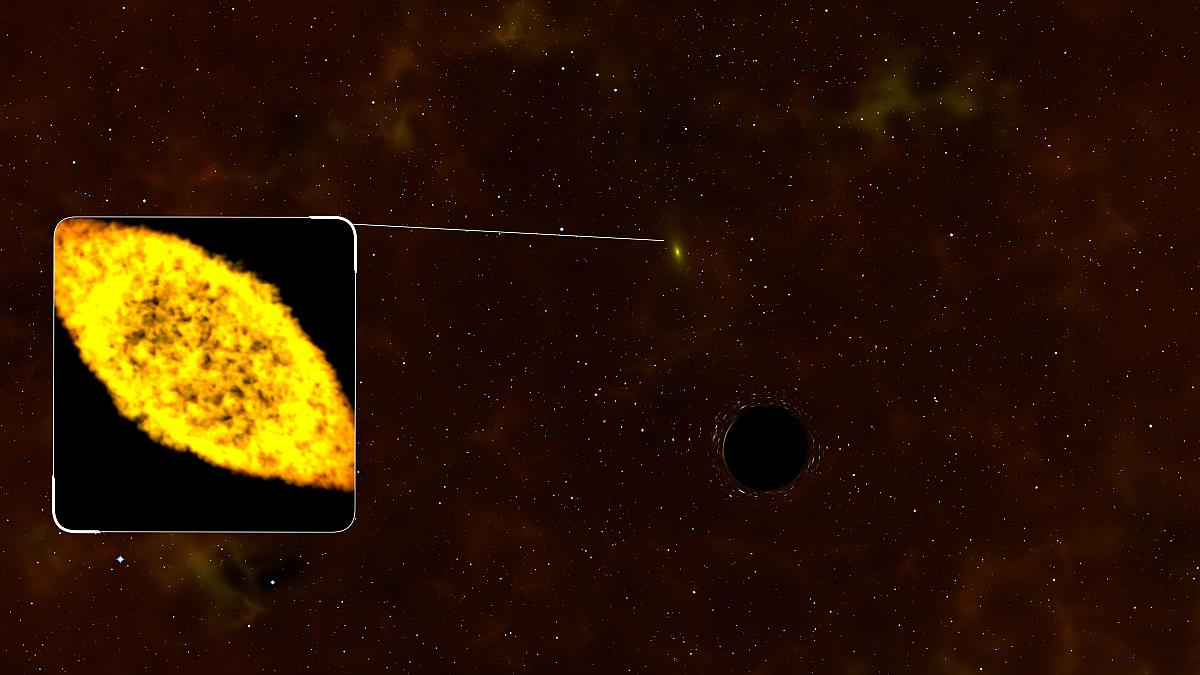
Whenever a comet makes a pass around the Sun, it loses some of its matter. The ices melt and the dust streams off in a tail. Inevitably, the comet will be reduced to a meteor or to celestial confetti, or resemble an asteroid, or a burned-out comet. Some comets collide with the Sun or a … Read more