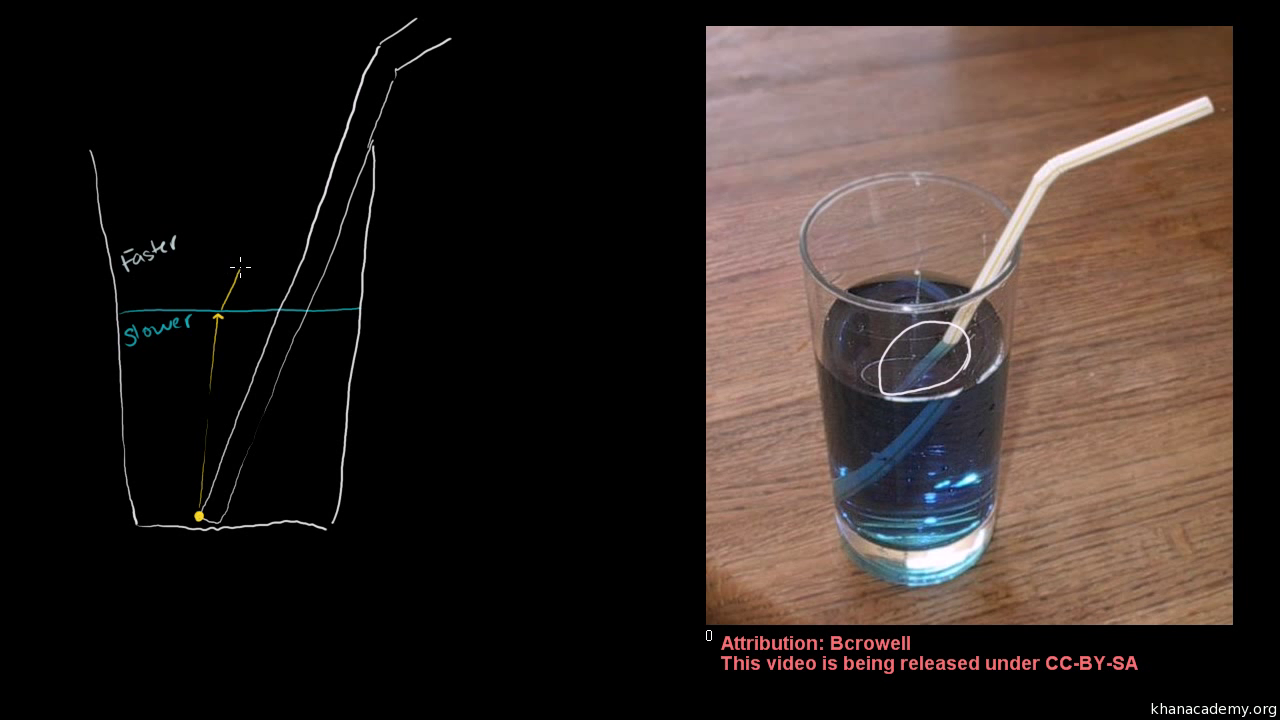
Why Are Ice Cubes Cloudier In the Middle Than At the Edges?
The cloudiness is a mass of tiny air bubbles, air that was dissolved in the water and expelled when the water froze. You can see the individual bubbles through a magnifying glass. There is always some air dissolved in any water that has been exposed to, well, the air. For this, the world’s fish are … Read more